Telehealth Reverse Diabetes For Safe Pregnancy | Free Trial In Texas

Diabetes affects both mother and unborn child. If pregnancy is a possibility, keep your weight down and exercise regularly.

Damage to the baby can happen before you even know you’re pregnant. Get ready for pregnancy, don’t just work on fixing your health after you become pregnant.
Let us help you control type 2 diabetes before pregnancy.
To learn more about programs Herd Healthcare offers, our website is:
www.herdhealthcare.com
Insulin Resistance During Pregnancy
Sugar is what the baby needs for energy. That sugar has to come from the mother’s blood and transfer to the baby across the placenta. The mother stores less sugar during pregnancy. The result is to increase levels of sugar in the mother’s blood. Insulin resistance keeps levels high enough to nourish the baby.
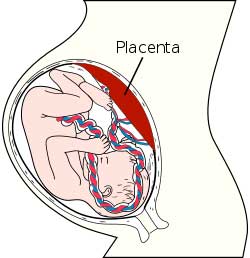 High levels of sugar are dangerous. If sugar levels are already high because of type 2 diabetes, further increase damages placental function and the baby’s development.
High levels of sugar are dangerous. If sugar levels are already high because of type 2 diabetes, further increase damages placental function and the baby’s development.
Transfer of fat and protein depend on normal function of the placenta. The problem is that high levels of sugar interfere with transfer.
Rates of growth by the baby also are affected by levels of sugar. Too much sugar makes organs grow too fast for normal function. Even too big for normal delivery when they’re born.
Gestational Diabetes
High levels of sugar and fat in the blood during pregnancy cause diabetes in about 5% of pregnancies in the US.
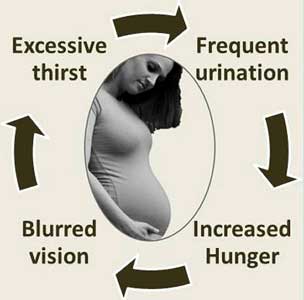 Symptoms of gestational diabetes are similar to symptoms of type 2 diabetes without pregnancy. Untreated, gestational diabetes causes excessive thirst, frequent urination, increased hunger and blurred vision. By the time these symptoms appear, insulin resistance is increased greatly. Consequently, high blood levels of sugar and fat are causing serious danger to normal growth and development of the unborn baby.
Symptoms of gestational diabetes are similar to symptoms of type 2 diabetes without pregnancy. Untreated, gestational diabetes causes excessive thirst, frequent urination, increased hunger and blurred vision. By the time these symptoms appear, insulin resistance is increased greatly. Consequently, high blood levels of sugar and fat are causing serious danger to normal growth and development of the unborn baby.
Rates of complications during pregnancy are increased. Also, these women and their babies have a higher than normal incidence of type 2 diabetes later in life.
Weight Gain During Pregnancy
 Some weight gain is important during pregnancy. Planning for pregnancy is when to lose weight. Not when already pregnant. Controlling blood sugar is what’s important during pregnancy.
Some weight gain is important during pregnancy. Planning for pregnancy is when to lose weight. Not when already pregnant. Controlling blood sugar is what’s important during pregnancy.
Takes 75,000 calories to make a baby. That’s 0 additional calories during the first trimester, 350 additional calories per day during second trimester and 450 additional calories per day during the last trimester. The total for the baby is about half of the total gain in weight to support a safe, healthy pregnancy.
 The U.S. Institute of Medicine recommends women of normal healthy weight should gain about 30 lb during pregnancy. That includes weight of the baby, placenta and the uterus. Additional weight of the mother includes body water. It is fluid weight of mother that provides blood and body fluids for the baby.
The U.S. Institute of Medicine recommends women of normal healthy weight should gain about 30 lb during pregnancy. That includes weight of the baby, placenta and the uterus. Additional weight of the mother includes body water. It is fluid weight of mother that provides blood and body fluids for the baby.
Rate of weight gain is a cause of gestational diabetes. Investigators in California actually have tested the rate of weight gain early in pregnancy as a cause of gestational diabetes in the second and third trimester.
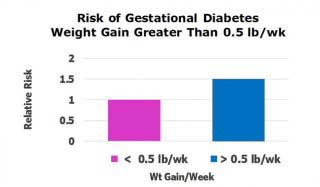 They tested glucose tolerance measuring glucose levels 3-hours after drinking a standard amount of sugar solution. They studied 354 women who later developed gestational diabetes and 800 women in a control group.
They tested glucose tolerance measuring glucose levels 3-hours after drinking a standard amount of sugar solution. They studied 354 women who later developed gestational diabetes and 800 women in a control group.
As shown in the Figure, women least likely to develop gestational diabetes gained less than about 0.5 lb per week during the first trimester. That was less than 7 lb in the first three months of pregnancy. Women who gained more than about 0.5 lb per week were 50% more likely to develop gestational diabetes later in pregnancy.
Pregnancy During Type 2 Diabetes
Danger from high levels of sugar in the baby’s blood has dominated the strategy for treatment of type 2 diabetes during pregnancy.
6-Step Guide To A Low Glycemic Diet Plan

 Efforts usually have been made to control blood sugar by eating food low in sugar and exercising at least 150 minutes per week.
Efforts usually have been made to control blood sugar by eating food low in sugar and exercising at least 150 minutes per week.
Since weight reduction is not advisable during pregnancy, choices of food to eat are extremely important. A low glycemic diet plan is recommended.
Almost always, oral anti-diabetes medication has been discontinued during pregnancy.
Insulin has been most widely prescribed as medication for control of blood sugar in type 2 diabetes during pregnancy. Insulin in blood does not cross the placenta from mother to baby.
Metformin also has been widely prescribed. In contrast to insulin, metformin does transfer to the baby’s blood. However, there have been no reports of dangerous effects from metformin on growth and development of the baby.
Anti-diabetic medication use during pregnancy has been studied in 7 different countries. Any use of anti-diabetes medication was 3% in over 5M pregnancies in all 7 countries. Use was about 5% in US and Australia.
When anti-diabetes medication was used before pregnancy, almost all prescriptions were discontinued or switched to insulin. When anti-diabetes medication was used for treatment of gestational diabetes, insulin was most always prescribed. In the US, glyburide was most often prescribed.
Recently, prescription of metformin has been greatly increased. Prescription of other anti-diabetes medications awaits further controlled clinical trials of their use.
Summary
Insulin resistance is gradually increased during pregnancy. Overweight and obesity present before pregnancy increase insulin resistance up to very high levels.
High levels of sugar are dangerous to the baby. High levels can damage placental function and the baby’s development.
Gestational diabetes occurs in about 5% of pregnancies in the US. Rates of complications during pregnancy are increased. Also, these women and their babies have a higher than normal incidence of type 2 diabetes later in life.
Some weight gain is important during pregnancy. The U.S. Institute of Medicine recommends that women of normal healthy weight should gain about 30 lb during pregnancy.
Rate of weight gain is a cause of gestational diabetes. Women who gained more than about 0.5 lb per week were 50% more likely to develop gestational diabetes later in pregnancy.
Danger from high levels of sugar in the baby’s blood has dominated the strategy for treatment of type 2 diabetes during pregnancy.
Insulin has been most widely prescribed as medication for control of blood sugar in type 2 diabetes during pregnancy. Recently, prescription of metformin has been greatly increased.
Let us help you control blood levels of sugar and fat before pregnancy.
 We are pleased to share our blog articles with you, and we are always interested to hear from our readers. Our website address is: www.herdhealthcare.com
We are pleased to share our blog articles with you, and we are always interested to hear from our readers. Our website address is: www.herdhealthcare.com




